Capture Settings are set-up separately for each capture channel. Once these settings have been specified, OK or Apply should be clicked. This tab specifies Echo settings.
Echo to Network Overview
ComCap can echo, remote or proxy any captured data to the network, using UDP (syslog), TCP Server or TCP Client protocols, which are detailed in the Networking Tutorial. Effectively, this allows ComCap to convert serial data to network protocols, to be captured on remote PCs for viewing or redundancy.
The various options that are enabled on this tab depend upon the 'Echo Type' setting on the General tab.
Using TCP Server, data may be echoed to a maximum of five remote PCs (using TCP Client) that connect to the Local IP Address and Port. Connections are refused for connections in excess of five. TCP Client and UDP need a remote IP address to be specified, and are thus limited to a single remote PC.
TCP/IP Client may also be used for 'IP Printing' using port 9100. Many network printers will accept print data on TCP/IP port 9100, although this will be plain text as captured, no attempt to send any control codes to the printer.
Echo to Remote - Local IP Address and Port
For TCP Server, this is the Local IP Address for server, selected from a drop down box, usually 0.0.0.0 and the IP Port on which the server will listen for remote TCP clients, usually higher than 1,024.
For UDP and TCP Client, the IP address should usually be 0.0.0.0 and the port set to zero so that Windows selects port randomly. A fixed port may be used to identify multiple UDP or TCP sessions from the same PC, but when a connection is lost there may be delay of several minutes before the port can be re-used.
SSL/TLS for Echo Client or Server
Tick this box if SSL/TLS is to be supported for either Echo TCP Server or Client, and further options will be enabled. TCP Client channels do not need any SSL certificates, but do need to decide whether to check they are connecting to the correct remote TCP Server with adequate security.
Echo to Remote - Remote IP Address and Port, Retry Attempts, Wait Seconds
For UDP and TCP Client, these fields allow the Remote IP Address and Remote IP Port to be specified, to which captured data will be echoed. They may not left blank or zeros. For UDP Syslog, the port is usually 514, for TCP Client it should be above 1,024, the same as that of the remote TCP Server which is listening.
UDP is an unreliable protocol where data is sent blind with no confirmation it has been received by the remote computer, which might not even exist.
TCP Client is reliable, and also needs Retry Attempts and Wait Seconds to be specified, so that connection attempts are repeated if they fail. Setting Retry Attempts to zero causes indefinite attempts to be performed.
SSL Client Echo Validate Remote Server Certificate
Specifies the remote SSL server certificate should be checked according to the settings in Common Settings, Common.
None |
No certificate takes place, may be needed for self signed certificates or privately issued certificates. |
PEM Bundle File |
A file supplied with ComCap containing about 289 certificate authority trusted root certificates in PEM format, essentially the same as used by Microsoft. Note over time old CA roots become disused and newer root certificates are issued (a couple a year), so this file can become obsolete over many years. The latest version of ComCap will have the latest root bundle file. |
Windows Certificate Store |
Windows has a dynamic certificate store, on new installations it's a few common CA root certificates, but further root certificates are automatically downloaded as needed to verify certificate chains. This may be a little slower than using the PEM Bundle File, particularly if a new root is needed, and may fail if the download fails. |
This is optional and does not prevent SSL being used, it may slow down connection set-up and potentially cause errors that prevent capture.
SSL Client Echo Security
Specifies the SSL security level to ensure that minimum SSL/TLS security standards are enforced. The options are:
None |
All protocols and ciphers, any key lengths |
SSLv3 Only |
SSLv3 only, all ciphers, any key lengths, MD5 hash |
TLSv1 Only |
TLSv1 only, all ciphers, RSA/DH private keys => 2,048 bits |
TLSv1.1 Only |
TLSv1.1 only, all ciphers, RSA/DH private keys => 2,048 bits |
TLSv1.2 Only |
TLSv1.2 only, all ciphers, RSA/DH private keys => 2,048 bits - recommended |
TLSv1.3 Only |
TLSv1.3 only, all ciphers, RSA/DH private keys => 2,048 bits |
TLSv1 or Better |
TLSv1 or later, all ciphers, RSA/DH private keys => 1,024 bits |
TLSv1.1 or Better |
TLSv1.1 or later, all ciphers, RSA/DH private keys => 1,024 bits |
TLSv1.2 or Better |
TLSv1.2 or later, all ciphers, RSA/DH private keys => 2,048 bits - recommended |
Backward Ciphers |
TLSv1 or later, backward ciphers, RSA/DH private keys => 1,024 bits, ECC keys => 160 bits, no MD5, no SHA1 hash |
Intermediate Ciphers |
TLSv1.1 or later, intermediate ciphers, RSA private keys => 2,048 bits, ECC keys => 224 bits, no RC4 ciphers, no SHA1 hash |
High Ciphers, 2048 keys |
TLSv1.2 or later, high ciphers, RSA private keys => 2,048 bits, ECC keys => 224 bits, no RC4 ciphers, no SHA1 hash - recommended |
High Ciphers, 3072 keys |
TLSv1.2 or later, high ciphers, RSA private keys => 3,072 bits, ECC keys => 256 bits, Forward Security forced |
High Ciphers, 7680 keys |
TLSv1.2 or later, high ciphers, RSA private keys => 7,680 bits, ECC keys => 384 bits, Forward Security forced |
The default security level is 'TLSv1.2 or Better' which is the PCI DSS council standard and recommended by major browsers. Generally the only reason to support old protocols or low security standards is to access 10 year or older servers that only supported those old protocols. Likewise, all SSL certificates have used 2,048 bit minimum private keys for several years and any older ones should have long expired (except some root certificates). The SHA1 hash was used to sign old certificates now replaced by SHA2 (aka SHA-256). Some SSL ciphers are potentially open to attack, but may still be needed to access very old servers that don't support anything better. Private keys with RSA 3,072 bits are the minimum recommended by NIST for use after year 2030, larger RSA keys increase the size of SSL certificates and thus the handshaking for each SSL connection.
Note if the security level is set too high, an SSL/TLS connection may just fail without any sensible explanation.
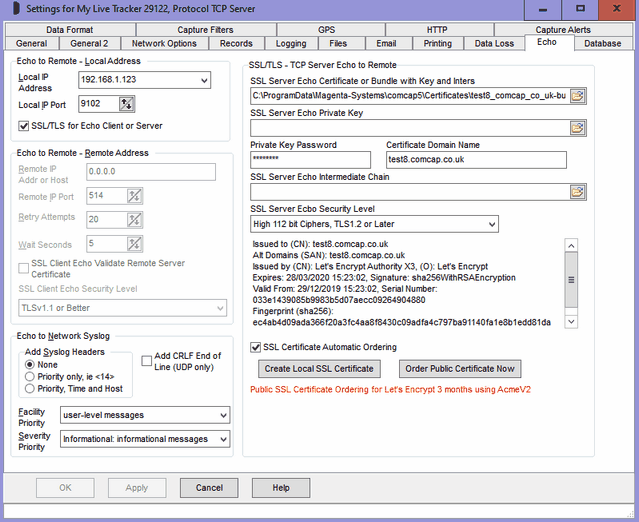
SSL/TLS - TCP Server Echo to Remote
TCP Server Echo must have a valid SSL/TLS certificate, or it will not start, see SSL/TLS and Certificates. The certificate may be shared with other channels or applications.
SSL Server Echo Certificate or Bundle with Key and Inters
Specifies the SSL/TLS server X509 certificate file, which may contain one or more certificates in various formats and a private key. Sometimes separate files are used for server certificate, private key and optional intermediate certificates, but using a bundle keeps them together for simplicity. The two bundle formats supported are PEM (which contains base64 ASCII) and PFX or P12 which is PKC12 binary format. Certificate only files may be PEM, DER, or P7 format. Sometimes PEM files have a CER extension.
If Automatic Certificate Ordering is enabled or Create Local SSL Certificate (see below) is used, this field may contain just a directory path for certificates, and ComCap will create a file name automatically using the Certificate Domain Name (see below) when one of the buttons below is clicked.
If this field is already completed, ComCap will display the certificate content in a scrolling window on this tab. The most important line is 'Issued to (CN)' which show the certificate Subject Common Name or domain name, which should match the 'Certificate Domain Name' field on this tab. Some certificates are valid for more than one domain name which are listed in 'Alt Domains (SAN)' Subject Alternate Names, or wildcard certificates where an * symbol matches any host (ie *.comcap.co.uk would match www,comcap.co.uk, test.comcap.co.uk, etc).
Note ComCap checks hourly for any new certificate files being available and will automatically load them without needing to restart the channel, provided the file names are unchanged.
SSL Server Echo Private Key and Password
If the SSL Server Certificate was not a bundle including a private key, allows a SSL Server Private Key X509 PEM file to be specified, see SSL/TLS and Certificates which must match the Servr Certificate. If the private key is encrypted, the password should be specified here, this also applies to bundles.
Echo Certificate Domain Name
Defaults to the PC host name which may include a domain, but needs to be the Domain Name assigned to the IP address of the TCP Server, for which the SSL/TLS server certificate has been issued. In the screen capture above, the Domain Name is test8.comcap.co.uk and this is the name that should be used to configure remote TCP Clients to send data to this server. Note the Domain Name can not be easily validated by ComCap, it is set-up in a DNS Server somewhere, not on this PC. For internal systems with internally issued certificates, the Domain Name may simply be the computer host name.
SSL Certificate Echo Intermediates
If the SSL Server Echo Certificate was not a bundle including intermediates, allows a default SSL Certificate Intermediate X509 PEM file to be specified, see SSL/TLS and Certificates. Most server certificates are signed by the supplier using an intermediate certificate, which is in turn signed by a trusted root CA certificate, so this intermediate needs to be supplied to allow the chain to be verified against a trusted root.
SSL Server Echo Security Level
Specifies the SSL security level to ensure that minimum SSL/TLS security standards are enforced. The options are:
None |
All protocols and ciphers, any key lengths |
SSLv3 Only |
SSL3 only, all ciphers, any key lengths, MD5 hash |
Backward Ciphers, TLS1 or Later |
TLSv1 or later, backward ciphers, RSA/DH private keys => 1,024 bits, ECC keys => 160 bits, no MD5, no SHA1 hash |
Intermediate Ciphers, TLS1.1 or Later |
TLSv1.1 or later, intermediate ciphers, RSA private keys => 2,048 bits, ECC keys => 224 bits, no RC4 ciphers, no SHA1 hash |
Intermediate Ciphers FS, TLS1.1 or Later |
TLSv1.1 or later, intermediate ciphers, RSA private keys => 2,048 bits, ECC keys => 224 bits, no RC4 ciphers, no SHA1 hash, Forward Security forced |
High 112 bit Ciphers, TLS1.2 or Later |
TLSv1.2 or later, high ciphers, RSA private keys => 2,048 bits, ECC keys => 224 bits, no RC4 ciphers, no SHA1 hash - default. |
High 128 bit Ciphers, TLS1.2 or Later |
TLSv1.2 or later, high ciphers, RSA private keys => 3,072 bits, ECC keys => 256 bits, Forward Security forced |
High 192 bit Ciphers, TLS1.2 or Later |
TLSv1.2 or later, high ciphers, RSA private keys => 7,680 bits, ECC keys => 384 bits, Forward Security forced |
TLSv1.2 or Earlier |
TLSv1.2 or earlier, intermediate ciphers, RSA private keys => 2,048 bits, ECC keys => 224 bits, no RC4 ciphers, no SHA1 hash, Forward Security forced |
TLSv1.3 Only |
TLSv1.3 only, intermediate ciphers, RSA private keys => 2,048 bits, ECC keys => 224 bits, no RC4 ciphers, no SHA1 hash, Forward Security forced |
While using the highest level of security is always best, this may prevent older clients connecting to ComCap. If clients attempt to connect with the latest TLSv1.3 protocol but fail, try setting security to 'TLSv1.2 or Earlier', the latest is not always the best. Note that the server SSL certificate must have a key length of the minimum the security level requires, or capture will not start. At the time of writing, the recommended default is 'High 112 bit Ciphers, TLS1.2 or Later', but this may change to 128 bit in a few years.
Create Local SSL Certificate
Allow a self signed local certificate to be immediately created for the Certificate Domain Name specified above, note doing this will replace any certificate files specified above. The X509 certificate will be created with the Private Key Type and Sign Digest specified in Common Settings, Network Options. Clicking the button will display a confirmation dialog, before creating self signed certificate bundles in PEM and PFX formats, with an encrypted private key with the specified password above, or 'password' if left blank. The file name field will be updated with the new file names, and the certificate details displayed. The SSL Server Certificate field must have at least a directory path specified, which will be used for system created file names. Details about certificate creation are shown in Network Options. Self signed local certificates allow SSL TCP Server channels to start, but any clients connecting to the server may get a warning or error message saying the certificate is not trusted, so such warnings will need to be disabled. For internal capture, such errors are usually acceptable.
SSL Certificate Automatic Public Ordering
If automatic free SSL/TLS X509 certificate acquisition and installation from Let's Encrypt has been specified in Common Settings, Network Options, ticking this box will enable it for this channel. The SSL Server Certificate field must have at least a directory path specified, which will be used for system created file names. The Certificate Domain Name must be available on the public internet and this TCP Server available from the public internet. Before issuing a certificate, Let's Encrypt will connect to a web server ComCap runs internally on port 80 of the same IP address used by the capture or echo channel, so public DNS must point to this IP address and there should not be any other web servers using it for validation will fail. The internal web server usually only runs for a few seconds during the certificate ordering process and while running ignores any requests other than from Let's Encrypt so is not a security risk.
Order Public Certificate Now
Let's Encrypt certificates only have a life of 90 days, and ComCap will automatically order a replacement before expiry, but a certificate may also be ordered here immediately for the Certificate Domain Name specified above. Clicking the button will display a confirmation dialog, before starting the order process, finally creating certificate bundles in PEM and PFX formats, with an encrypted private key with the specified password above, or 'password' if left blank. The file name field will be updated with the new file names, and the certificate details displayed. The SSL Server Certificate field must have at least a directory path specified, which will be used for system created file names. Details about certificate creation are are shown in Network Options.
Echo to Network Syslog
Syslog is a specific streaming format with predefined fields, with some options set below.
Add Syslog Headers, Priority (Facility/Severity) Text
Specifies that syslog headers should be added to echoed lines:
Priority Only |
<14> is a Priority value where the first 7 bits of the number are a facility code and the last 3 bits are severity, selected from the drop down Facility Priority and Severity Priority lists. The Actual Priority text that will be added is show, |
Priority, Time and Host |
Also add the time and host and program name, similar in format to: <14>Mar 25 17:03:04 PC09 ComCap |
Note that Syslog headers are normally only used with UDP.
Add CRLF End of Line (UDP only)
This tick box specifies whether echoed UDP lines should have CRLF added to the end of each captured line. The TCP protocols always have CRLF added for end of line.